CHOOSE_E
Contents
function choose_E(obj,tangentModes)
choose_E
This function defines the master modal subspace and performs resonance analysis. Its input is an array of indices, which indicate the set of modes over which the invariant manifold is to be computed.
if isempty(obj.System.spectrum) [~,~,~] = obj.System.linear_spectral_analysis(); end % tangent eigenvalues nLambda = numel(obj.System.spectrum.Lambda); lambda_M = obj.System.spectrum.Lambda(tangentModes); % normal eigenvalues normalModes = setdiff(1:nLambda,tangentModes); lambda_S = obj.System.spectrum.Lambda(normalModes); % define subspace E obj.E.spectrum = lambda_M; obj.E.basis = obj.System.spectrum.V(:,tangentModes); obj.E.adjointBasis = obj.System.spectrum.W(:,tangentModes); % determine whether resonance occurs obj.resonance = resonance_analysis(lambda_M,lambda_S,obj.Options.reltol);
end
Resonance Analysis
function [resonance] = resonance_analysis(lambda_M,lambda_S,reltol)
The purpose of this function is to check exisitence and uniqueness of the SSM by evaluating the non-resonance conditions between the (master and slave) modal subspaces.
It is assumed that the inputs
 are given in the form of column vectors.
are given in the form of column vectors.
m = length(lambda_M);
Zero tolerance for detecting near resonances:
ref = min(abs(lambda_M)); if ref<1e-10; ref = max(abs(lambda_M)); end abstol = reltol*ref;
Maximum order upto which resonance would be checked:
sigma_in_max = 10;
sigma_out_max = 10;
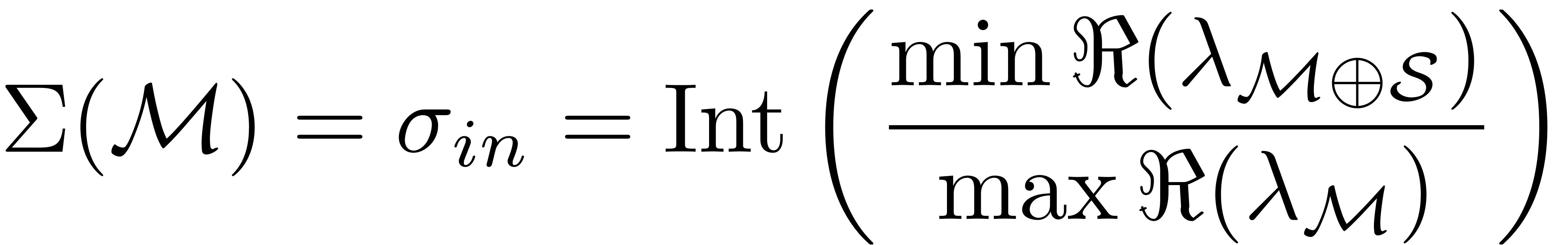
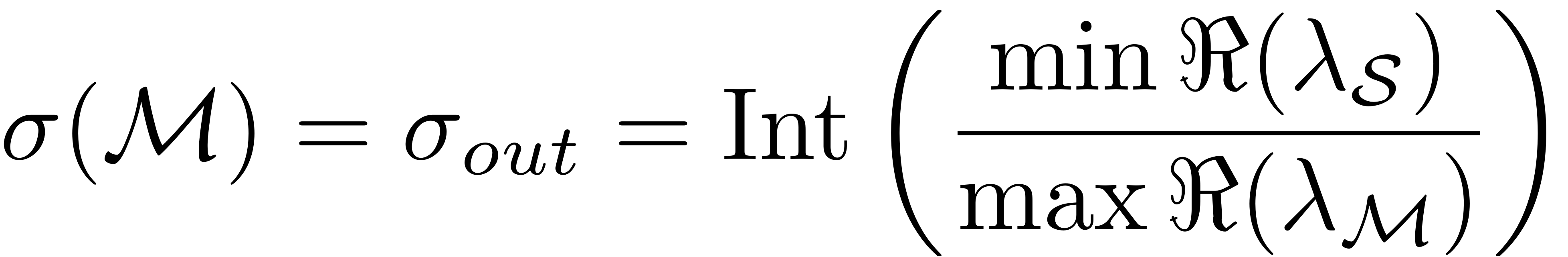
When the SSM is constructed around the slowest subspace, then we
have
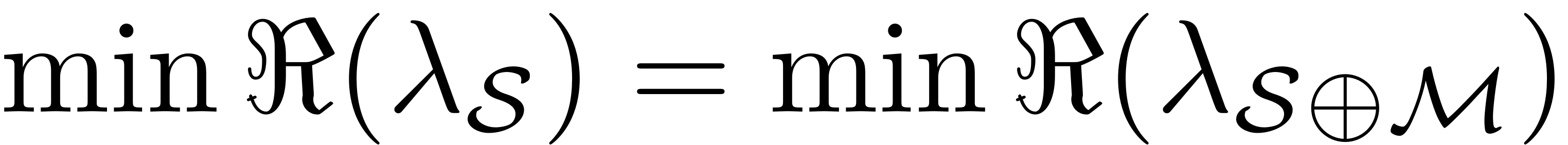 and
and
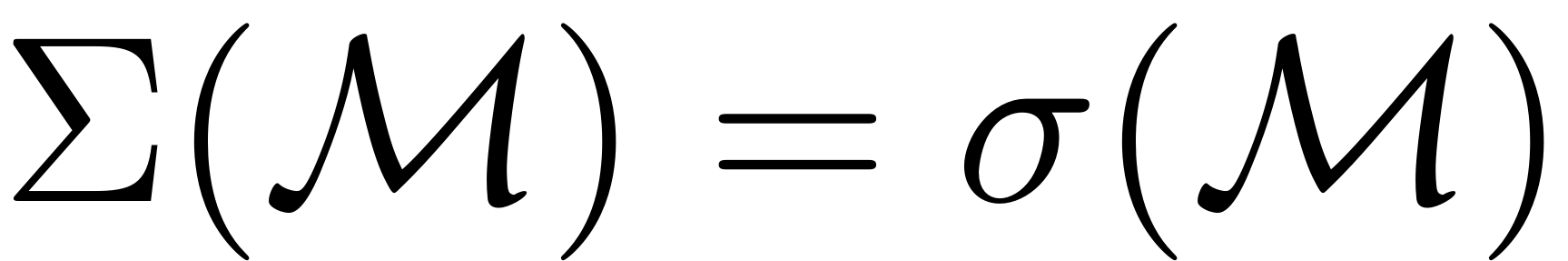 .
.
Note that for 2-dimensional underdamped SSMs,
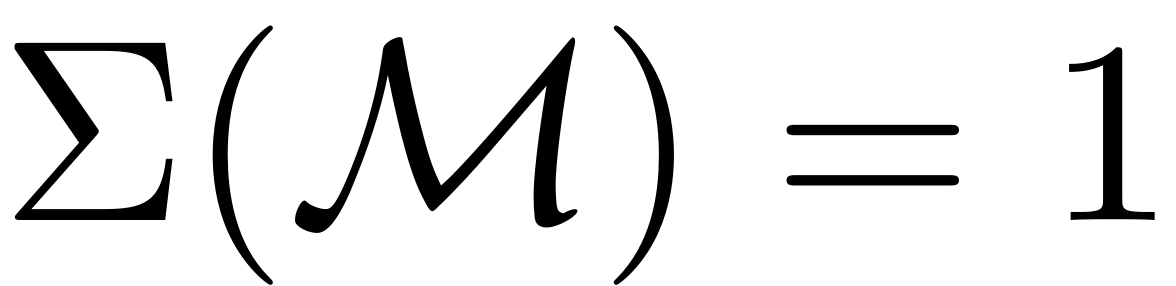 according to the above formula.
according to the above formula.
lambda = [lambda_M;lambda_S]; sigma_in = fix( min(real(lambda)) / max(real(lambda_M)) ); if isempty(lambda_S) sigma_out = 0; else sigma_out = fix( min(real(lambda_S)) / max(real(lambda_M)) ); end
Checking for (near) outer resonances
if sigma_out < 2 % no outer (low-order) resonances can occur resonance.outer.occurs = false; else
Compute
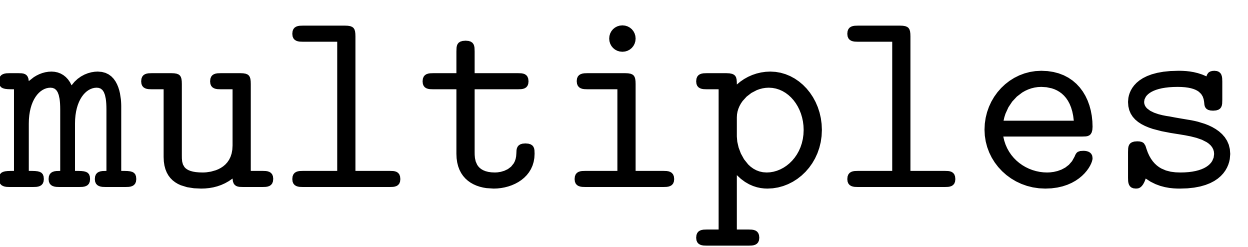 of the resonant modal subspace that add up to
of the resonant modal subspace that add up to
 , i.e., rowsum of each row in
, i.e., rowsum of each row in
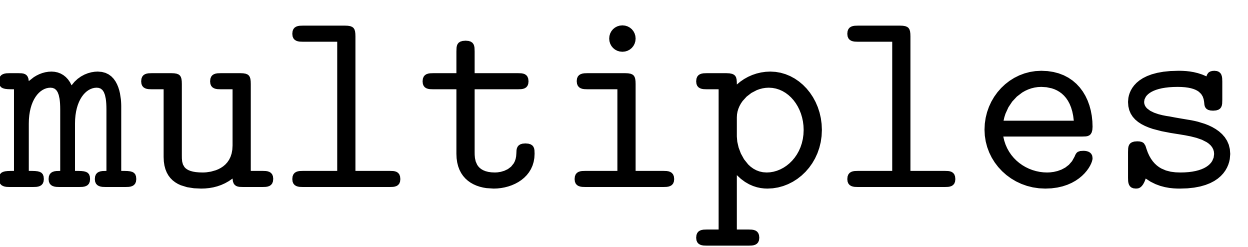 is less than or equal to
is less than or equal to
 .
.
sigma_out_check = min(sigma_out_max,sigma_out);
range = 2:sigma_out_check;
multiples = [];
for order = range
multiples_j = nsumk(m,order,'nonnegative'); % returns non-negative m-tuples summing ...
% exactly equal to order.
multiples = [multiples; multiples_j];
end
Compute integer combinations: If
 is a column vector containing the eigenvalues
is a column vector containing the eigenvalues
 of the master modal subspace
of the master modal subspace
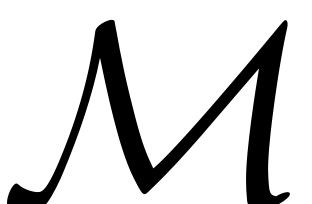 , then
, then
 gives a column vector containing non-negative integer combinations
of these eigenvalues.
gives a column vector containing non-negative integer combinations
of these eigenvalues.
combinations = multiples * lambda_M;
n_combinations = length(combinations);
COMBINATIONS = repmat(combinations,[1 length(lambda_S)]);
LAMBDA_S = repmat(lambda_S.', [n_combinations, 1]);
[I, J] = find(abs(COMBINATIONS-LAMBDA_S)<abstol);
if any(I)
resonance.outer.occurs = true;
disp('(near) outer resonance detected for the following combination of master eigenvalues')
resonance.outer.combinations = multiples(I,:);
disp(resonance.outer.combinations)
disp('These are in resonance with the follwing eigenvalues of the slave subspace')
resonance.outer.eigs = lambda_S(J);
disp(resonance.outer.eigs)
else
disp('No (near) outer resonances detected in the (truncated) spectrum')
resonance.outer.occurs = false;
end
end resonance.outer.sigma = sigma_out; disp(['sigma_out = ' num2str(sigma_out)])
Checking for near-inner resonances
if sigma_in < 2 % no inner (higher-order) resonances can occur resonance.inner.occurs = false; else
Compute integer combinations: If
 is a column vector containing the eigenvalues
is a column vector containing the eigenvalues
 of the master modal subspace
of the master modal subspace
 , then
, then
 gives a column vector containing non-negative integer combinations
of these eigenvalues.
gives a column vector containing non-negative integer combinations
of these eigenvalues.
sigma_in_check = min(sigma_in_max,sigma_in);
range = 2:sigma_in_check;
multiples = [];
for order = range
multiples_j = nsumk(m,order,'nonnegative'); % returns non-negative m-tuples summing...
% exactly equal to order.
multiples = [multiples; multiples_j];
end
combinations = multiples * lambda_M;
n_combinations = length(combinations);
COMBINATIONS = repmat(combinations,[1 length(lambda_M)]);
LAMBDA_M = repmat(lambda_M.', [n_combinations, 1]);
[I, J] = find(abs(COMBINATIONS-LAMBDA_M)<abstol);
if any(I)
resonance.inner.occurs = true;
disp('(near) inner resonance detected for the following combination of master eigenvalues')
resonance.inner.combinations = multiples(I,:);
disp(resonance.inner.combinations)
disp('These are in resonance with the follwing eigenvalues of the master subspace')
resonance.inner.eigs = lambda_M(J);
disp(resonance.inner.eigs)
else
disp('No (near) inner resonances detected in the (truncated) spectrum')
resonance.inner.occurs = false;
end
end resonance.inner.sigma = sigma_in; disp(['sigma_in = ' num2str(sigma_in)])
end
