COMPUTE_FEXT
function fext = compute_fext(obj,t,x,xd)
This function computes the external force at a particular time t in a second-order mechanical system.
The quasiperiodic second order system force is given as a Taylor expansion on coordinates of the physical coordinates:
![$$ \mathbf {f}(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{\phi}) = \left[\begin{array}{c} f^1(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{\phi})
\\ \vdots \\ f^{n}(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{\phi})\end{array}\right], \quad
f^i(\mathbf{x},\mathbf{\phi})
= \sum_{\mathbf{n}\in \bf{N}^{n}}
f^i_{\mathbf{n}}(\mathbf{\phi}) \mathbf{x}^\mathbf{n} $$](compute_fext_eq15419072546320047766-Rescaled.png)
The force coefficients are given as a fourier expansion in terms of
the phase variable
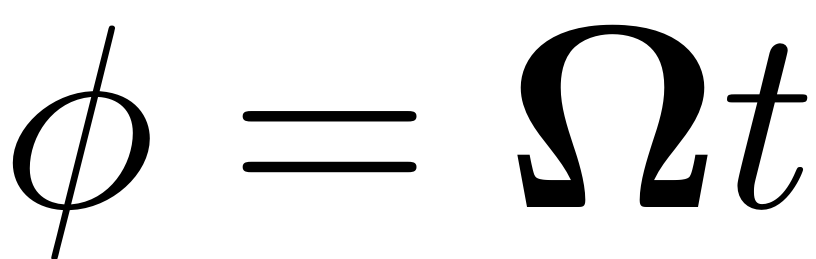
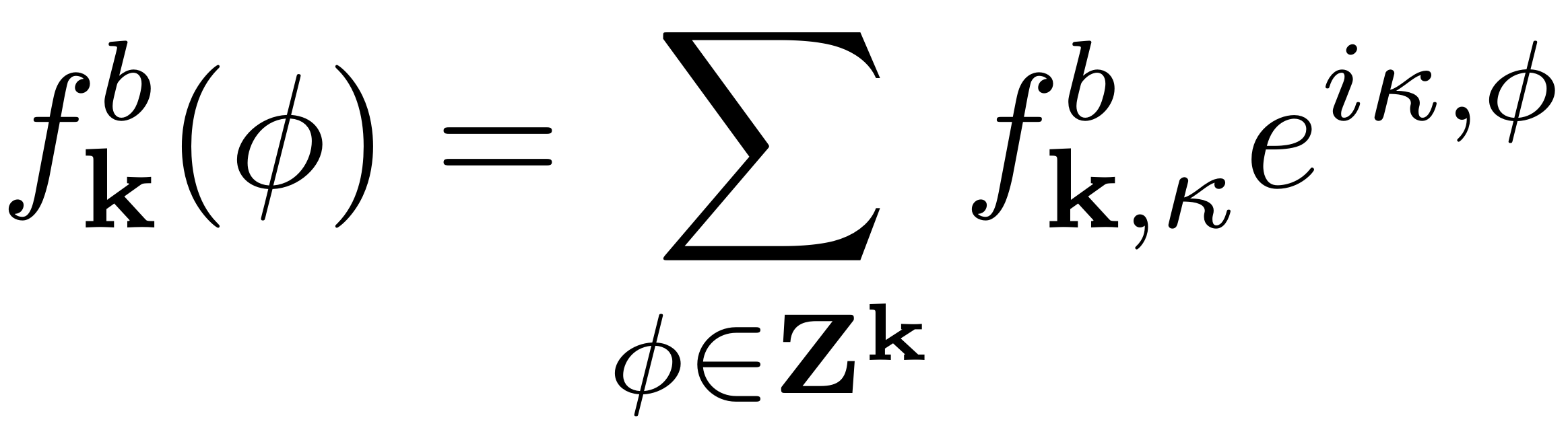
assert(obj.order == 2, ' fext can only be computed for second-order systems') if isempty(obj.fext) fext = sparse(obj.n,1); else assert(~isempty(obj.Omega), ' fext cannot be evaluated as the Omega property of the DS class is empty') % This function assumes periodic forcing nt = size(x,2); fext = zeros(obj.n,nt); nKappa = obj.nKappa; for i = 1:nKappa % Highest order this Force contributes at order = numel(obj.fext.data(i).f_n_k)-1; % zeroth order f0 = obj.fext.data(i).f_n_k(1); if ~isempty(f0) && ~isempty(f0.coeffs) fext = fext + real( f0.coeffs * exp(1i * obj.fext.data(i).kappa * obj.Omega .* t)); end for j = 1:order % array starting at 0 %Contribution to order j Forcing with harmonic kappa_i fij = obj.fext.data(i).f_n_k(j+1); if ~isempty(fij) && ~isempty(fij.coeffs) if size(fij.ind,2) == obj.n fext = fext + real(expand_multiindex(fij,x) .* exp(1i * obj.fext.data(i).kappa * obj.Omega .* t)); else fext = fext + real(expand_multiindex(fij,[x;xd]) .* exp(1i * obj.fext.data(i).kappa * obj.Omega .* t)); end end end end assert(size(obj.Omega,2) == size(obj.fext.epsilon,2),'epsilon and Omega must have same number of columns'); fext = fext * diag(obj.fext.epsilon); if obj.Options.BaseExcitation fext = fext*diag((obj.Omega).^2); end end
